There may not be a recipe for success, but we’ve noticed there’s surely one for failure — trying to sell to everyone.
Not everyone needs your product or service. So, there’s no point in promoting your product or service to anyone who’s NOT your target market.
In all our years as marketers, we saw many businesses wasting time, effort, money, and resources when they didn’t define their target market. So, we thought of sharing everything we know about how to market your business to the right audience.
Let’s get started.
What is Target Market?
Your target market is a specific group that has the maximum chance of becoming a paid customer or client. In other words, these are your ideal customers.
Here’s what you should know about target markets:
- They’re a segment of the entire market that’s most likely to respond and convert to your offers;
- They’re identified based on shared characteristics, needs, wants, behaviors, pain points, or demographics;
- They help businesses gain insights into customers’ motivations, pain points, and desires;
- They help streamline and optimize marketing messaging, offers, unique value propositions, and more.
A conventional target market definition states that it is a group of people identified as potential customers for a product because of their shared traits such as age, income, or lifestyle.
As a business owner, your goal should be to maximize your reach among your target audience. This helps your demand generation efforts, reduces the cost of customer acquisition, and improves the chances of conversions.
Benefits of Defining a Target Market
Knowing your target market helps you focus your marketing efforts where they matter most. Here’s why defining an ideal target market is essential:
- Better understanding. Gain insights into customer motivations, needs, and pain points for more personalized marketing strategies;
- Increased relevance. Personalize your messaging and efforts to meet the specific preferences of your audience;
- Personalized marketing. Design strategies that resonate with your audience throughout the customer journey;
- Efficient resource allocation. Save time and money by targeting only those most likely to engage with your business;
- Competitive advantage. Stand out with unique offerings designed for your chosen customer segment;
- Higher conversion. Address audience needs directly, increasing the chances of turning prospects into customers.
Key Components of a Target Market
Defining your target market isn’t just about knowing who your customers are—it’s about breaking down their unique traits and behaviors to connect with them on a deeper level.
Target marketing segmentation helps you categorize your audience into groups, which you can use to personalize your marketing campaigns.
Simply put, segmentation is the process of grouping prospective customers based on key characteristics to resonate with their unique needs, preferences, and buying habits.
Here are the key components you can utilize to segment your target market:
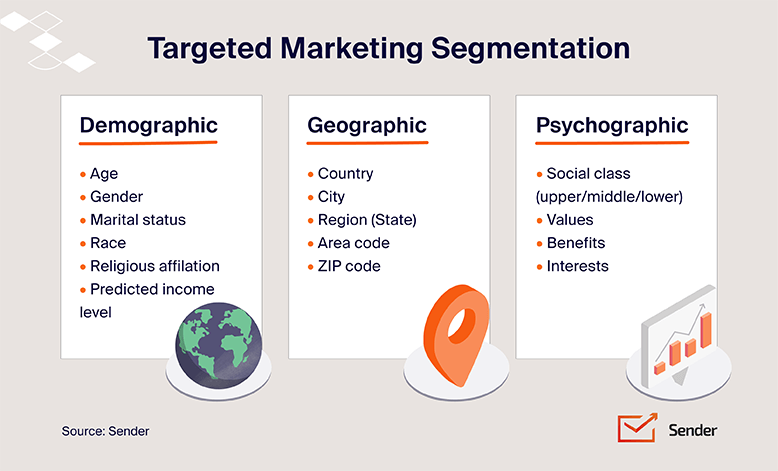
1. Demographic Segmentation — Who Are These People?
Ever wondered why different age groups respond to the same product in entirely different ways?
Enter demographic segmentation. It’s a crucial factor in defining and grouping your target customers.
Demographics include personal characteristics, like:
- Age;
- Gender;
- Income;
- Education;
- Occupation;
- Marital status;
- Ethnicity, etc.
Want to make the most of demographic insights? Start segmenting your email list with Sender’s powerful tools and watch your campaigns soar.
2. Geographic Segmentation — Where is Your Audience?
Does location really matter in marketing? Spoiler alert: It absolutely does.
Geographic attributes refer to the location or the specific geographical areas in which the target market resides. It involves splitting your target market into segments based on their location.
This can be highly useful for businesses looking for geographic targeting. For example, a bakery can group customers within a 10-mile radius for a local marketing campaign.
Some examples of geographic attributes include:
- Country;
- Region;
- City;
- Neighborhood;
- Urban or rural audience;
- International audience.
3. Psychographic Segmentation — Why Your Audience Buys?
What drives your audience to make a purchase? Their values, lifestyle, and beliefs hold the key.
Psychographic segmentation focuses on understanding the psychology and motivations behind actions.
It involves analyzing beliefs, values, interests, lifestyles, attitudes, and motivations, and designing marketing messages that speak to them. A great example can be an eco-friendly brand focusing on environmentally conscious consumers.
Psychographic segmentation includes traits such as:
- Beliefs and values;
- Interests and hobbies;
- Lifestyle;
- Attitudes and opinions;
- Motivations and aspirations;
- Personality traits.
4. Behavioral Segmentation — How Your Audience Buys?
Behavioral segmentation groups your target audience based on their actions and usage patterns. Basically, how they interact with products, brands, or services, and purchasing habits.
These are then used for creating hyper-targeted campaigns like sending a limited-time offer to shoppers who abandoned their cart midway or running a win-back campaign to bring inactive customers back.
Here are some behavioral factors which can be used to segment your target market:
- Purchasing frequency;
- Purchase occasion;
- Email engagement rate;
- Website activity;
- Social media interactions;
- Content downloads;
- Add to wishlist.
How to Define Your Target Market?
Defining your target market is an important part of the marketing mix and is like piecing together a puzzle — you need to gather the right data and dig deeper to draw useful insights.
Here’s how you can get started with defining the target market for your business:
Market Research
Market research sets the foundation for understanding your target market. It involves collecting data about potential customers, understanding market trends, and spotting gaps you can fill.
Tap into available resources like NAICS codes or market research providers to gain valuable insights. Surveys and interviews with your customer base provide direct input, while tools like industry reports add context to your findings.
Here’s how to start with market research:
- Conduct online surveys to gather firsthand consumer data;
- Use tools like Google Trends to identify emerging market needs;
- Analyze social media conversations to spot trending topics or concerns;
- Utilize NAICS codes for industry-specific trends and market size.
Analyze Your Existing Customers
Your current customers are your best resource for understanding what’s already working. Studying their behavior helps identify shared traits and purchase patterns that can shape your target audience.
For example, look at your repeat buyers or those who engage the most with your marketing. Segment this data to refine your future campaigns.
Here’s how to get started with target market analysis:
- Survey loyal customers to uncover why they choose your brand;
- Segment your database by demographics, purchase frequency, or product preferences;
- Identify trends like common age groups or regions with high engagement;
- Analyze website and social media analytics to spot patterns in user behavior.
Use Competitor Analysis
Your competitors are targeting a similar audience—what can you learn from them? By analyzing their strategies, you can uncover gaps, opportunities, and ways to set yourself apart.
Look at their product offerings, customer engagement tactics, and reviews. Use tools like SEMrush during competitive analysis to track traffic sources and insights that drive their marketing success.
Here’s what you should do to analyze competitors:
- Study competitor websites and social media platforms for target audience insights;
- Use tools like SEMrush or SimilarWeb to analyze their traffic sources;
- Identify gaps in their strategies and craft campaigns to fill those gaps;
- Monitor customer reviews to learn what buyers love or dislike.
Create Customer Personas
Customer personas are fictional representations of your ideal customers. They combine data from your research and analysis to help you visualize who you’re targeting. These customer profiles act as guides for creating differentiated marketing campaigns.
Each persona should highlight key traits, motivations, and challenges. This clarity ensures your marketing resonates with your audience’s unique needs.
Here’s how to define your ideal customer profile:
- Create a buyer persona based on real data from surveys and analytics;
- Name your personas for easy identification (e.g., “Tech-Savvy Tara” or “Budget-Conscious Ben”);
- Include specific details like preferred communication channels and buying triggers;
- Regularly update personas as the market evolves.
Examples of Target Market
You must’ve got a good idea about target markets by now. Let’s examine how big brands define their target markets to drive their marketing and brand strategy.
Target Market for Nike
Nike is popular globally for their high-quality shoes, apparel, and sports accessories. Their market positioning focuses on quality and durability. With a high price point, it’s essential for them to target individuals with high disposable incomes.
So, they target athletes and sports enthusiasts, especially young runners and aspiring athletes with disposable income. They focus on delivering high-quality products that motivate individuals to push beyond their limits.
Nike’s digital marketing campaigns and action-oriented content on platforms like Instagram resonate with their audience’s drive for achievement. Have a look:

Target Market for Apple
Apple is renowned for its innovative product design and wide range of offerings. Their products cater to diverse audiences, like:
- Tech enthusiasts & creators who value cutting-edge technology like Apple Watch and HomePods;
- Healthcare professionals who benefit from the seamless communication capabilities of iPhones and iPads.
But that’s not the only target market for Apple. They target multiple segments at once while maintaining consistent brand communication and delivering value.
Overall, Apple positions itself as a brand for people who want to make a difference. Their ability to appeal to multiple demographics with the same products is a cornerstone of their success.
Target Market for Starbucks
Starbucks targets a diverse yet specific target market, focusing on urban professionals, millennials, and Gen Z who value premium coffee and a cozy café experience.
With its warm ambiance, free Wi-Fi, and digital rewards programs, Starbucks positions itself as a “third place” between home and work, attracting customers who seek more than just coffee—a lifestyle.
Check out one of their recent campaigns:
Their products appeal to individuals willing to pay a higher price for quality, convenience, and personalization.
Target Market for Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola’s diverse product portfolio targets a large global audience. Their primary target market includes younger customers aged 10-25, with a secondary target market comprising people aged 25-40.
Regular cola appeals to those seeking bold flavors, while diet options target health-conscious individuals.
Coca-Cola’s non-cola drinks, like Sprite, attract teens and college students, showcasing their strategy of expanding product lines to cater to different tastes. This broad targeting ensures their relevance across various age groups and preferences worldwide.
Target Market FAQs
What are target market types?
Target markets can be of different types, including Mass Market (broad, diverse audiences for mass marketing), Broad Market (large but slightly focused groups), Niche Market (specialized, smaller segments), Micromarket (personalized segments for hyper-local targeting), and Specific Market (precisely defined based on detailed traits).
What’s the difference between target market and target audience?
A target market is a broad group of potential customers for your product or service, while a target audience refers to a specific subset of that market for which a campaign is being created. For example, a target market could be young adults, and the target audience might be tech-savvy students aged 18-24.