Knowing your audience better can turn this year super profitable for your business.
You’re marketing your product or service, but you cannot sell to EVERYONE. Therefore, everything you do is laser-targeted towards attracting and closing that one “ideal customer” type, aka your target audience, someone who needs your product or service and is more than happy to pay money to get it.
Target audiences are essential in marketing. So let’s learn everything about it, including the benefits of getting to the right target market and how to find your target audience.
What is Target Audience — A Simple Definition
How do you define a target audience? Target audience refers to a specific group of people most likely to buy from you. You should ideally target these people during each marketing campaign. They’re your ideal prospect or, simply put – the intended audience.
These people are most likely to show interest in your product, service, or business and become your customers in the future.
You may have one or more target audiences depending on your exact business. Generally, you’ll find two types of target markets — the known audience and the unknown audience.
Unknown audiences are the ones who’re between the awareness and consideration stages of the buyer’s journey — they may or may not know about you. The known audience is the one that knows about you’re might be thinking of buying from you.
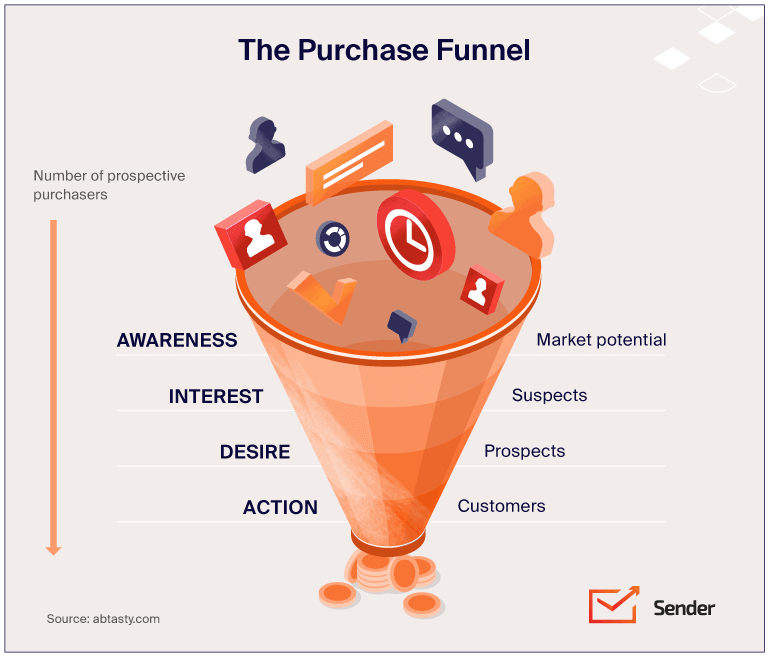
Benefits of Defining Your Target Audience
Most people are not your prospects, even when it seems like it. The truth is you will get maximum success when you’re only selling to a tiny percentage of online users — your target audiences. This small and focused group of people will most likely trust you because you have exactly what they need.
Defining your target market offers the following advantages as a business owner:
- Improved Marketing Messages. The better you understand your prospects, the better you can talk to them in a language they understand. Your marketing speaks to their pain points and concerns directly. This leads to more relatability and, ultimately, higher customer loyalty.
- Better ROAS Due To Focused Ad Targeting. Laser-targeted ads for target audiences are guaranteed to convert better, leading to higher returns on ad spending for your eCommerce stores.
- Higher Conversions Over Email Marketing. Once you nail your “Customer Avatar” or “Buyer Persona” down, your emails will register increased open rates, higher deliverability, and increased replies and conversions.
- Stand Out From Competition. Audience definition improves your personalization efforts. This will help you become more relatable and stand out from the competition, as 76% of consumers love buying from businesses that personalize their marketing efforts.
Identifying who could be most interested in your products or services and targeting them directly improves the chances of a sale.
Find and reach your ideal audience—segment, craft perfect emails in minutes, and engage the right people without a hassle.
Free plan available for up to 2,500 subscribers and 15,000 emails per month!
Types of Target Audiences
Most businesses will likely deal with multiple “types” of ideal prospects — e.g., when your product solves a problem common to both working women and college students.
We segment our target audience into different “Customer Avatars” or “Buyer Personas” when this happens. This segmentation can happen based on various considerations. Some of the key ones are as listed below:
- Audience Demographics: Age, Gender, education level, Income levels, marital status, parenthood status, subcultures based on race or religion, etc.
- Psychographics: Core Values, personal beliefs, hobbies & pass time activities, professional interests, Personality types, lifestyle choices, etc.
- Habits & Behaviors: Purchase intent, living habits, engagements, interactions, etc.
- Geographics: Local businesses, Same city or state, Particular country or international targeting, etc
- Existing Customer: A group of individuals who are already customers of a business or organization and who may be targeted with loyalty or upselling campaigns.
- Prospective Customer: A group of individuals who have not yet purchased from a business or organization but who may be interested in doing so in the future.
- Niche Audience: A smaller, highly specialized group of individuals with specific needs or interests.
- Mass Market: A very large, diverse group of individuals with broad interests or needs.
Examples of classification of target audiences:
- Age range – e.g., 25-40 yrs old
- Gender – e.g., Female audience only for a beauty make-up product
- Location of residence – e.g., living in and around New York City only
- Education Level – E.g., Graduates only
- Socioeconomic status – E.g., iPhone or Mac users only
- Income Levels – E.g. earning at least $1,00,000 yearly
Often finer niches and more granular groups are referred to as Subcultures, while theming these Subcultures under the leading target group leads us to a Superculture.
Analyzing the Types of Target Audiences
Now that you already know the types of target audiences, let’s look more in detail at what defines each one:
Demographics
The term demographics refers to the broad range of data that describes a person or group. Demographic factors include age, gender, nationality, ethnicity, etc.
These factors can be used to divide your target audiences into different target groups to give you a better understanding of who they are and what they want.
Demographic segmentation helps businesses target their customers based on gender, age, income level, etc., and become more effective. Some examples of demographics include:
- Age;
- Gender;
- Education level;
- Income levels;
- Marital status;
- Parenthood status, etc.
Interests
Interests help marketers segment their audience into different groups that share similar interests.
Target audiences divided into groups based on interests can be used for sharing customized offers, personalized content, or marketing messages you want to send to them. Here are some examples of different interests:
- Fitness;
- Technology;
- Entertainment;
- Travel;
- Financial security;
- Education, etc.
Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior refers to the behavior patterns of people most likely to use your products and services. For example, expecting mothers may be more likely to buy a product that helps them avoid nausea and fatigue.
Consumer behavior mapping is an important part of any marketing campaign, as it identifies which audiences need different kinds of messages and how to deliver them. You can map consumer behavior by asking the following questions:
- What products does the target market consume? What products do they need?
- How do they behave?
- Why are they buying the products?
- Which media channels do they use?
- What information do they seek out?
- How often do they shop?
- What stage are they in?
- Where are they most likely to go next?
- Who do they talk to?
You can also segment your audience based on their behavior by tracking their online behavior.
Metrics such as follows can help you find your target audience based on consumer behavior:
- Purchase intent;
- Living habits;
- Engagements;
- Interactions, etc.
Product Specific Behavior
Marketers often use the product usage patterns or behavior of previous customers to inform future product choices. Product usage patterns or behavior can help you create past and current customer personas, which helps you better understand their needs and desires.
You can use these personas to identify and segment your target market. For example, you can create content and marketing campaigns based on product usage patterns and behavior to target a specific audience.
For example, if you have a loyalty program, you can create segments based on the frequency with which your users log in, whether or not they sign up for a reward, and how much they spend per visit.
Target Audience Examples
You’re likely filled with ideas about how to find and document your target audience. Let’s clear your brain with a real target audience example from a hypothetical business idea.
Let’s say you run a Shopify Store offering custom-printed T-shirts. Your product targets young males, and you plan to advertise this over Meta/Facebook. You have identified this specific target audience example based on your product.
You wouldn’t want to show everyone the identical ad copy and creatives. So, you need a focused target audience. In this target audience example, you can segment your audience based on age and interests. You may want to target young males between 18-25 who have shown an interest in fashion and streetwear.
By identifying this target audience example, you can create targeted ads and messaging that will appeal to this specific group. This approach can help you increase the effectiveness of your advertising and improve your return on investment.
Let’s see what kind of audiences you can identify depending on your objectives:
1. Intended Target Audience
Intended audience meaning is more straightforward than you might’ve thought – it’s the group of people for whom your services and products are made.
This is also a relatively “primitive” audience, i.e., it’s usually identified only by two demographic characteristics: age and gender. Take a look at the target audience analysis below.
Basic audience segmentation will look like this:
- Gender: Male
- Age Group: 15-25 yrs
From here, you can start narrowing down your primary target audience; think about what other characteristics could be shared by 15-25 years males. For example, as it’s a younger crowd, we assume they might be interested in music bands, pop culture, and Japanese anime.
2. Primary Target Audience
By looking at possible characteristics that your intended audience shares, you can further create two sets of your primary target audience. Following the target audience analysis example from above, your audience for Meta ads would look something like this:
Audience Set 1
- Gender: Male
- Age Group: 15-25 yrs
- Interests: Music bands, Pop culture.
You can further experiment with target market analysis and fiddle with audiences’ interests.
Audience Set 2
- Gender: Male
- Age Group: 15-25 yrs
- Interests: Computer games, Japanese anime.
Multiple target audience sets can be tested to understand who’ll likely buy your product. This is a classic example of testing out uncharted waters — you have an assumption of your audience and use real users to validate your assumptions. Based on insights, you can optimize your product, positioning, and marketing strategy. This way, you can also find different target audiences for your future campaigns.
For example, the product design can have multiple color and messaging variations by age group and gender – cool and funky messages for the younger and more hip crowd and simple creative ones with polite messaging (if any) for the older crowd.
3. Cold Audiences
Once you’re done with audience analysis and have defined different sets of your primary target audience, consider its relation to your brand, products, and services. Do the people in the audience know anything about you? If yes, have they already bought from you?
A person who’s most likely never heard of your brand before belongs to a cold audience. Usually, these people are the most challenging and costly to convert into customers. The two reasons for that are:
- Before deciding to purchase, a person has to recognize the brand at a certain level;
- Reaching these users demands paid marketing efforts, like running Facebook ads.
And yet, businesses must recognize cold audiences as gaining new customers is crucial for the long-term growth of any business.
So, how do you include cold audience targeting in your business strategy? Honestly, it’ll be rough from the beginning since you’re unlikely to have contact data. That said, you have two broad options:
- Investing in advertising on traditional marketing channels like radio, print, and television that can be costly and demand you commit longer.
- Aiming your marketing efforts to Google Ads and Facebook Ads that are considered the best performers in new customer acquisition.
Other marketing efforts like organic Facebook posting and email campaigns might’ve been a part of your successful marketing strategy in the past. Unfortunately, without some strong incentive to be shared by your current customers with non-customers, they have little to no impact on cold audiences.
4. Warm Audiences
A warm audience consists of people who’ve already come across your brand: engaged with your socials or have purchased from your website. Compared to a cold audience, this audience is much easier to advertise since they already know your brand.
As you don’t have to invest in your brand introduction, with warm audiences, you’ll want to educate more about your product or services. Luckily, they’re cheaper to target and respond at a much higher rate in comparison with colder audiences. Another great thing about marketing to warmer audiences is that since it consists of your prospects (the users are already defined), they can be targeted both on social media and via email.
Smaller businesses especially tend to gravitate towards targeting warm audiences rather than cold ones since they consider it more effective due to a higher ratio of work to ROI. However, focusing only on warmer audiences is inadvisable as future revenues are much more impacted by the Customer Lifetime Value of targeting colder audiences.
In other words, targeting prospects with a strong interest in the brand’s products is likely to bring more revenue but shorter-term gains than targeting cold audiences.
5. Customers
Further down the marketing funnel, you’ll find the audience of customers who’ve already purchased from you.
Most likely, they’ve become your customers due to targeted marketing efforts in the past, so the strategy aimed at getting the attention of your current customer base is called email remarketing or retargeting.
In remarketing campaigns, the customer is re-engaged based on their past behavior, like buying a specific product, visiting a particular page on your website, or expressing their interest in a product category in an online form.
If your customers need a little push to purchase from you again but don’t follow you on social media and never open your emails, remarketing can help by various means. One well-known approach is banner ads, when website banners follow the tagged customers where they often visit: local media outlets, YouTube, forums, and others.
Another approach that gained immense popularity in the last decade is Facebook Ads. Here remarketing is done via ‘Custom Audience.’ To take advantage of Facebook’s custom audiences, you must upload your customer data or set up Facebook Pixel. Once done, you can email custom audiences of people who visited your website but didn’t leave their contacts.
It should be noted that remarketing is still an additional expense in your business strategy, even if much less costly than other types of advertising.
6. Target Demographics
Though considered highly inadvisable due to low effort and unimpressive results, as a last resort, some businesses may consider targeting an audience defined by a single demographic characteristic.
Let’s take as an example a fictional situation of a small business that decided to sell grooming and shaving products. Since the brand is new, they might still need to learn what specific audience they should target. So, they decide to target all males.
Targeting only one demographic like this might work to some degree. After all, males are a vast audience likely to use shaving products. However, being half of the world’s population makes it more of a shot in the dark.
8 Ways to Determine Your Target Audience
There’re a million ways to identify and segment your target audiences. But the more you read about them, the more you get confused.
Remember, finding your target audience isn’t rocket science; you must keep the basics in mind. The first thing you need to do is study your customer demographics and gather feedback from your audience. Next, you can also study market trends and research the industry. Also, it’s important to assess your competition and determine what they’re doing that’s successful.
Here’s a step-by-step plan to determine your target audience:
1. Study Your Customer Demographics & Gather Feedback
Studying your existing audience and demographic data is the best place to start finding who your target audience is.
Your email marketing tool or AI writer could already have some information about your audience. You can track how many people open each message, how long they stay on your website, what products they’ve viewed, etc. Use this information to get a broad-level picture of who’s your ideal customer.
You can also look at information from your CRM, sales data, analytics, or other marketing tools.
Once you’ve studied and identified a user group, you can reach out directly to them to understand what they want.
Conduct a small survey to understand what are their pain points and if you can solve them. Ask your existing audience for their feedback about your product or service. Some questions to include:
- What do you want from our product?
- What do you love about it?
- What do you dislike about it?
- How did you find us?
- Does it solve any of your everyday problems?
- Is there anything else you would like us to know?
For example, if you’re running a blog and eComm store about fashion and beauty tips, you might have a mix of regular visitors who come to read posts and shoppers who want to buy from you.
Ask your current visitors what they want to see in your blog, and ensure you deliver those updates. Also, try to find out what you could improve in your strategy. Your existing audience may have already identified areas that you need to improve. Use all this information to segment your audience further and target similar user groups.
2. Research Market & Industry Trends
Market research is essential to your success as an entrepreneur or business owner. The data helps you understand what your customers want, who these customers are, how you can solve their problems, and if they’ll pay for it.
Market research and analyzing industry trends are one of the best ways to reach your target market.
You can use tools like Google Trends, Ahrefs Market Explorer, GapScout, etc., to learn more about your customers and industry. These tools will help you conduct market research, understand growth trends, and unearth patterns to bring you closer to your audience.
How?
You can use this information to add to your marketing strategy when you know about trends and patterns. The result — people who get attracted to growth trends within your industry are more likely to interact with your brand, too.
You can then use the new users to conduct thorough audience research, as mentioned previously.
3. Assess Your Competition
One of the most effective ways to get closer to your target audiences is to spy on your competitors. Analyze what your competitors are doing and if that’s working for them.
Analyze their marketing strategies and tactics, then be inspired by creating your own that will help you reach your target market.
Ask yourself — what are they doing to attract their audiences?
For example, if your competitors run paid ad campaigns and raise sales revenue, you could experiment with paid ads to find your target audience.
The most important thing here is to determine your competitor’s core competency and then find out how you can stand out from them.
Once you have determined your competitor’s core competency, you can make informed decisions about how to compete against them. Remember, uniqueness in your marketing strategy will only be achieved if you know what others are doing.
Here are some ways you can find out what your competitors are doing:
- Google the keywords you plan to focus on. This will show you all the pages your competitors have indexed, how much traffic they get, and any mentions on social media platforms;
- Check the ‘top results’ on the SERP for your competitors. Take note of where they rank, what they’re ranking for, and what kind of links they have;
- Use the SEO tools to see what links your competitors are ranking for;
- Find out if they’re using Facebook, Twitter, or other social media ad campaigns;
- Find out what social channels they’re using. This can tell you what audiences they’re targeting and which platforms they’re most active on.
All this will show you the kind of effort you need to make to bring your audience closer to you. In other words, the information you gathered till now will help you create a character sketch of your audience.
4. Develop Profiles of Ideal Customers (Buyer Personas)
A buyer’s persona is a written profile about your ideal customer. Think of it as a resume of your ideal customer, but in the context of what you want to know about them.
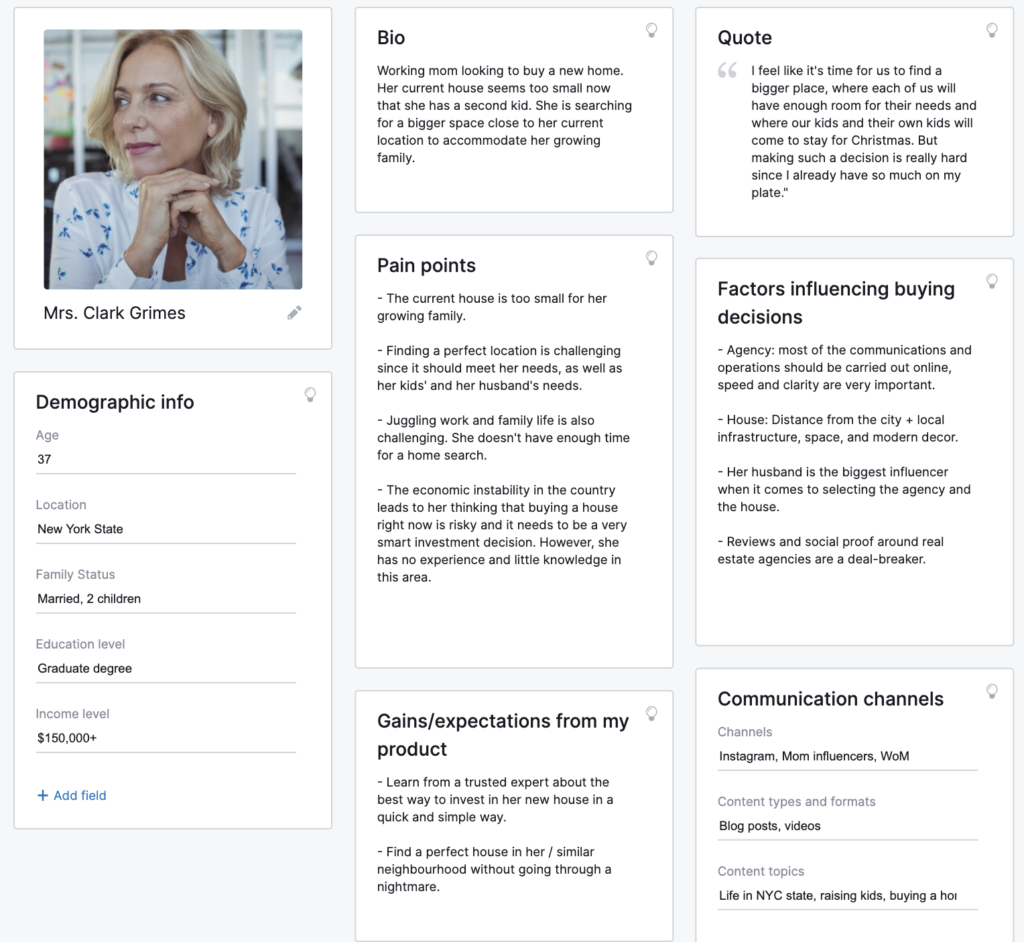
Imagine how valuable this information can be for your marketing strategy, right?
Now, use the information you gathered in the abovementioned steps to start profiling the ideal customer. You can use online tools to discover and document your target audiences.
The key is to develop customer personas that cover all aspects of the buyer journey, including demographics, interests, personality traits, and motivations, as in the example above.
An ideal buyer persona is a combination of three components:
- Demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and occupation)
- Psychographic information (such as personality traits and values)
- Behavioral information (such as preferred online and offline media)
To test your marketing campaigns, you can use a persona template to create a targeted audience, such as a younger female professional with two children with a monthly income of $50k or more.
Your buyer personas will act as a guide to help you become more relatable, valuable, and customer-centric. As you feed more data into your audience personas, you will realize how much you know about them and can use it to make them stop scrolling or open your email.
Here’s how you can create buyer personas for your business:
- Describe your ideal customer;
- Get feedback from people like your ideal customer;
- Collect data about their interests, behaviors, and motivations;
- Use the data to write down how you think the customer might feel and act in certain situations (psychographics).
- Use the information to develop a persona that captures the behavior, motivations, and emotions that your audience would have in each situation.
- Make product, pricing, marketing, and content strategy decisions based on the buyer persona.
Developing accurate buyer personas or profiles can help you determine the type of content you should produce and the marketing channels.
5. Identify Negative Market Segments
When it comes to identifying which audience you’re targeting, it’s important to remember that the same message can’t persuade different people.
You must use customer segmentation strategies to identify people you don’t want to target.
Here are some tips for you to consider:
- Know who you don’t want to reach. For example, if your product is location specific, ensure you don’t waste time targeting people in a different location.
- Take advantage of analytics. Use a tool like Google Analytics to find the general demographic profile of people who abandon the cart the most. Then slowly try to nurture them using automation, and if you don’t get good results, remove them from your target audiences.
- Find out about the price sensitivity of your product. Run a small test to find how much users will pay for your product. If a particular segment is unwilling to pay your expected price, consider them a negative segment and start focusing on less price-sensitive users.
Removing negative segments from your target markets will help you bring down your customer acquisition cost (CAC), register higher open/conversion rates on your emails, and overall have more relatability to your core target user group. To have better performance for emails, it’s useful to apply conversion rate optimization solutions.
6. Keep Updating & Refining Your Target Audience Personas
Your target audience is constantly changing. To keep your marketing efforts relevant to your audience, regularly reviewing and refining your target audience is vital.

Use data to improve your understanding of your audience. Conduct regular surveys and keep an eye on emerging market trends.
You can refine your audience personas through a variety of means, such as:
- Analyzing their activity on your site;
- Optimizing their demographics profile, and;
- Using social listening tools to find out about their thoughts and concerns.
7. Utilize Google Analytics To Track Audience Data
Google Analytics is one of the most popular tools for tracking visitors and analyzing your web visitor data. It will help you learn about your audiences and help you understand the trends on your site.
Use it to gain insights into their audiences, monitor their activity, and optimize your target group’s marketing strategies. You can get the following information about your target market using Google Analytics reports:
- The demographics of your audience;
- Where is your audience coming from;
- How they’re finding your site;
- Which pages is your audience visiting the most;
- How many people visited your site last month vs. last year, and a lot more.
Google Analytics provides you with an excellent starting point to analyze the data that has been collected on your website. You can use this data to understand if visitors are converting into buyers, which kind of visitors are most likely to buy from you, which platforms work best for your business, and more.
All this data is great for improving your buyer persona and refining your target audience strategy.
8. Use Similarweb To Get More Information
Similarweb is a competitive research platform that can give you insights about visitors and audiences for all your competitors. SimilarWeb provides traffic data for millions of websites, which is useful for determining your audience. You can use SimilarWeb to find:
- Traffic volume of a competitor’s website;
- Average visit duration;
- Top referring domains;
- Number of unique pages visited;
You can use SimilarWeb to find your target audience’s interests and passions. People visiting the same website, again and again are most likely interested in their offerings.
You can use all these insights to improve product and service offerings and become more relatable. For example, if you want to know how much money or time customers spend on Amazon, you can use Similarweb to get similar information about Amazon and its competitors.
The possibilities are endless. You need to focus on getting the maximum amount of data.
4 Easy Ways to Reach Your Target Audience
‘How to reach my target audience?’, you might ask. We know that it’s a huge challenge and requires much more than finding your audience. You need to get active on multiple platforms and create relevant content to get their attention. Here are four marketing channels you can use to reach your audience and your target market:
1. Email
Emails are an easy way to stay connected with your customers. Also, email can be the most effective way to reach your target audience. According to a recent study, two out of three marketers use email to distribute content organically.
You should also use emails to reach out to your audience from time to time. You can plan a newsletter, share offers, and/or nurture leads to become your customers through email.
Here’s what you should have in mind when using email marketing to engage your target audience:
- Build email lists. You can do it with email opt-in forms offering lead magnets (eBooks, special discounts, guides, etc.). Once you have a quality email list, segment it according to specific customer characteristics and use them to target separate audiences effectively.
- Personalize your emails. Take a closer look at your target audience and address their needs with personalized content or offer. It’s the straightest way to boost customer engagement.
- Invest in email design. It doesn’t matter how patiently a personalized email is crafted; chances are it will go unnoticed if presented in an unattractive package. Luckily, most email marketing tools, like Sender, come with a drag-and-drop builder and premade templates, allowing you to create visually captivating emails in no time.
Use marketing automation tools like Sender to ease your work while achieving more. With Sender, you can set up and automate email marketing campaigns with a super simple workflow builder.
No time to craft an email from scratch? No worries! You can create one in minutes with Sender’s drag-and-drop builder and premade templates:
2. Blog Content
Blogs are critical in helping you bring in new customers. However, while it’s great to see traffic numbers on your website growing, to build trust and authority among your prospects, you have to “text target” them with content they can relate to.
So how do you reach the right audience with the right content? Follow these tips:
- Understand your audience. To offer better-tailored content, look at simple demographic points: location, age, and job title. Then ask yourself about their current challenges, routines, and goals, and use this information to craft your content. Finally, collect insights to enhance your topic strategy as you learn more about your content readers.
- Research. Learn where your audience looks for information (Community forums? Media outlets? Social media platforms?). Visit and revisit those places to understand what your readers are discussing there. Then bring that discussion to your website.
- Prepare in advance. Ensure you have a constant flow of content your target audience will love. In return, you’ll get a continuous flow of returning readers.
- Employ your readers. Notice your recurrent readers and encourage them to recommend you. Offer them an attractive incentive: recognition, discount, or gift, and watch them build your audience for you.
Pro tip: If your blog has quality content covering several topics, it might also interest the general audience. ‘General audience’ meaning is people who aren’t a part of your target audience.
3. Social Media
Social media is a simple way to spread the word about your business. Social media platforms have become the largest search engine on the internet, which has a vast potential to drive users to your website.
Plus, you can quickly build a loyal following that you can use to test your ideas, gather more understanding of your audience, and use push sales.
So, if you already have an audience you want to target on social media in mind, what’s the next logical step to take in reaching out? Finding the best ways to do it, of course:
- A/B testing. Create content that differs in elements, formats, and publishing times and test to see what works the best. Notice the patterns in posts your target audience engages with and use this knowledge to optimize your social media content strategy.
- Content for each stage of the marketing funnel. Catch the attention at the awareness stage with entertaining content, but consider switching to more in-depth pieces when targeting the audience at the consideration phase.
- Active listening. Don’t trust your analytics one hundred percent. You can really know your audience if you talk to them. Consider conducting polls and asking direct questions. Use the received information to paint a more detailed picture to engage your customers better.
4. Video Marketing
Video marketing continues to be an effective and popular method of attracting your target audience. All you need to create relevant videos that reach potential customers and target your audience is a solid narrative account on a video platform, a great concept to push daily content, and some video editing tools.
That said, here are the top tips for video marketing on how to increase customer satisfaction and boost target audience engagement in return:
- Find your platform. You’ll find different audiences and engagement rates on different platforms, so spend time choosing a platform frequented by your target audiences and fitting your goals. For example, TikTok is great for reaching younger audiences, while LinkedIn is reserved for more professional ones.
- Tell a captivating story. We’re a species of storytellers, so the better the story and the bigger the emotional impact, the bigger the engagement. Research the best way to convey your message through storytelling and use it to connect with your audience.
- Keep it concise. People don’t like to watch long videos. That’s a fact. Think of the best way to convey more with less and engage your viewers with short clips, animations, and infographics.
- Remember to include CTA. Don’t leave your viewers hanging, and encourage them to take action – visit your website or purchase a product with a verbal message, on-screen text, or a clickable link.
Key Takeaways
- You need to define target market and reach it with contextual offers and content to stay relevant;
- Knowing more about your target market improves your marketing effectiveness;
- Target audience discovery is an ongoing process;
- Online tools and automation can save you much time reaching out to your audience.
Also read:
